How Early Learning Activities Shape a Child’s Brain Development
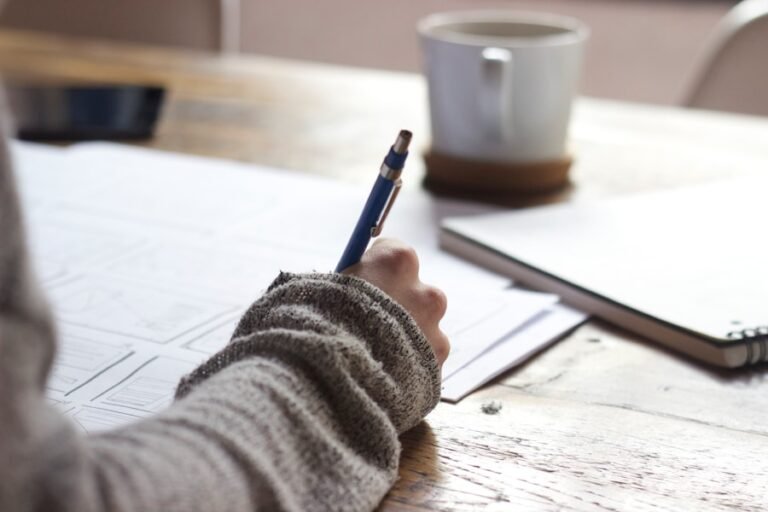
Early learning activities are crucial for the development of young children. These activities encompass a wide range of experiences that help children learn and grow, including play, exploration, and interaction with their environment. From birth to age five, children undergo rapid brain development, and early learning activities play a significant role in shaping their cognitive, social, and emotional development.
These activities can take place in various settings, including home, preschool, and daycare, and they are essential for laying the foundation for future learning and success. By engaging in early learning activities, children can develop essential skills such as problem-solving, creativity, and social interaction, setting the stage for a lifetime of learning and growth.
The Importance of Early Learning Play for Brain Development
Play is a fundamental aspect of early learning activities and is essential for brain development in young children. When children engage in play, they are actively using their brains to explore, imagine, and problem-solve. Play allows children to make sense of the world around them and develop essential cognitive skills such as memory, attention, and language. Research has shown that play is crucial for the development of neural pathways in the brain, which are essential for learning and processing information.
Furthermore, play provides opportunities for children to practice and refine their motor skills, spatial awareness, and sensory processing. By engaging in various types of play, such as imaginative play, constructive play, and physical play, children can strengthen their brain development and lay the groundwork for future academic success.
How Play Affects Cognitive Development
Play has a profound impact on cognitive development in young children. When children engage in play, they are actively using their brains to explore, imagine, and problem-solve. Through play, children can develop essential cognitive skills such as memory, attention, and language. For example, when children engage in imaginative play, they are using their creativity and imagination to create new scenarios and storylines, which helps them develop their language and communication skills.
Similarly, when children engage in constructive play, such as building with blocks or puzzles, they are honing their problem-solving skills and spatial awareness. By providing opportunities for children to engage in various types of play, parents and educators can support their cognitive development and help them build a strong foundation for future learning.
The Role of Play in Social and Emotional Development
In addition to cognitive development, play also plays a crucial role in social and emotional development in young children. Through play, children learn important social skills such as cooperation, empathy, and conflict resolution. When children engage in pretend play, they have the opportunity to take on different roles and perspectives, which helps them develop empathy and understanding for others. Play also provides opportunities for children to practice social interactions and learn how to navigate relationships with their peers. Furthermore, play allows children to express their emotions and develop emotional regulation skills.
For example, when children engage in physical play, they have the opportunity to release pent-up energy and emotions in a safe and constructive way. By providing opportunities for children to engage in various types of play, parents and educators can support their social and emotional development and help them build strong relationships with others.
Types of Play and Their Impact on Brain Development
There are various types of play that have a significant impact on brain development in young children. Imaginative play, also known as pretend play or make-believe play, allows children to use their creativity and imagination to create new scenarios and storylines. This type of play helps children develop their language and communication skills as they engage in role-playing and storytelling. Constructive play involves activities such as building with blocks, puzzles, or other manipulative materials.
This type of play helps children develop their problem-solving skills, spatial awareness, and fine motor skills. Physical play involves activities that allow children to move their bodies and develop their gross motor skills. This type of play is essential for developing strength, coordination, and balance. By providing opportunities for children to engage in various types of play, parents and educators can support their brain development and help them build a strong foundation for future learning.
Incorporating Play into Early Learning Environments
It is essential to incorporate play into early learning environments to support the brain development of young children. Parents and educators can create environments that are rich in opportunities for play by providing a variety of materials and activities that encourage exploration and creativity. For example, setting up a dramatic play area with costumes and props can provide opportunities for imaginative play. Similarly, providing open-ended materials such as blocks, clay, or art supplies can support constructive play. Outdoor spaces with playground equipment can provide opportunities for physical play. By creating environments that support play, parents and educators can help children develop essential skills and lay the foundation for future learning.
Nurturing Brain Development Through Play
Early learning activities are crucial for the development of young children. Play is a fundamental aspect of early learning activities and is essential for brain development in young children. Through play, children can develop essential cognitive skills such as memory, attention, language, problem-solving, creativity, social skills such as cooperation, empathy, conflict resolution, emotional regulation skills such as expressing emotions in a safe way. By providing opportunities for children to engage in various types of play such as imaginative play, constructive play, physical play parents and educators can support their brain development and help them build a strong foundation for future learning.
Read Also: From the UK to the USA: Navigating Travel with a Student Visa
It is essential to incorporate play into early learning environments to support the brain development of young children by providing a variety of materials and activities that encourage exploration and creativity such as dramatic play area with costumes and props open-ended materials such as blocks clay art supplies outdoor spaces with playground equipment. By creating environments that support play parents and educators can help children develop essential skills and lay the foundation for future learning.